点击查看目录
作者:钟华,腾讯云容器产品中心高级工程师,热衷于容器、微服务、service mesh、istio、devops 等领域技术
今天我们来解析 istio 控制面组件 Pilot, Pilot 为整个 mesh 提供了标准的服务模型,该标准服务模型独立于各种底层平台,Pilot 以插件方式对接不同的服务发现平台,解析用户输入的流控配置,转换为统一的服务发现和流量控制模型,并以 xDS 方式下发到数据面。
Pilot 译为领航员, 在 mesh 中负责路由领航,是 istio 控制面的核心组件。
在组件拓扑中,Pod istio-pilot包括istio-proxy(sidecar) 和discovery2 个容器,pilot 核心能力由容器 discovery中执行的命令pilot-discovery discovery提供。
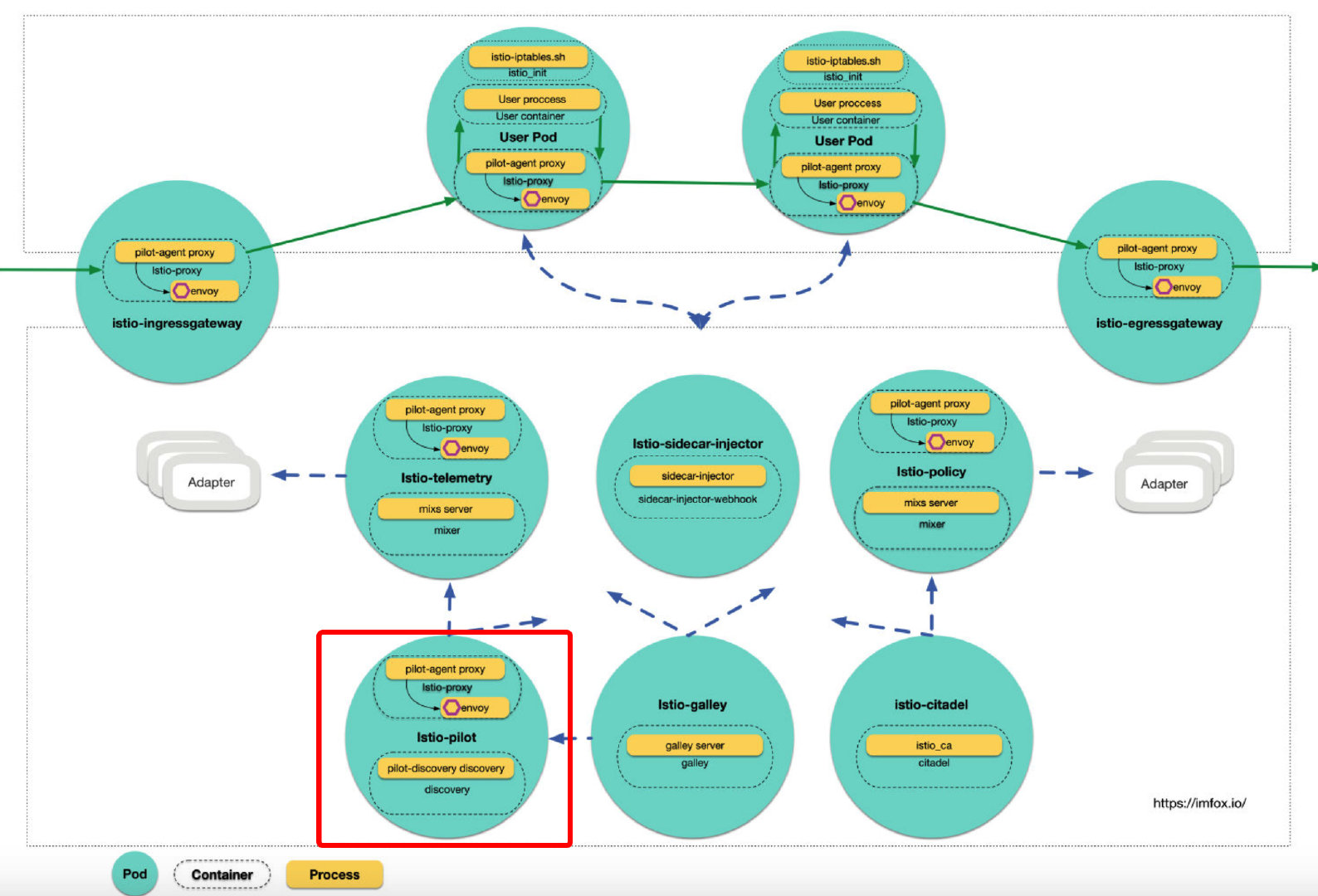
在源代码中,package github.com/istio/istio/tree/master/pilot/cmd 有三个命令的入口:
- sidecar-injector: 在前面文章中有过介绍。
- pilot-discovery: 控制面 pilot 核心服务,本文重点分析。
- pilot-agent: istio 里 sidecar 中主进程,用于启动和管控 envoy, 后续文章中进行分析。
1. Pilot 设计
下图展示了当前 istio(1.1.X) 中 Pilot 的流程设计:
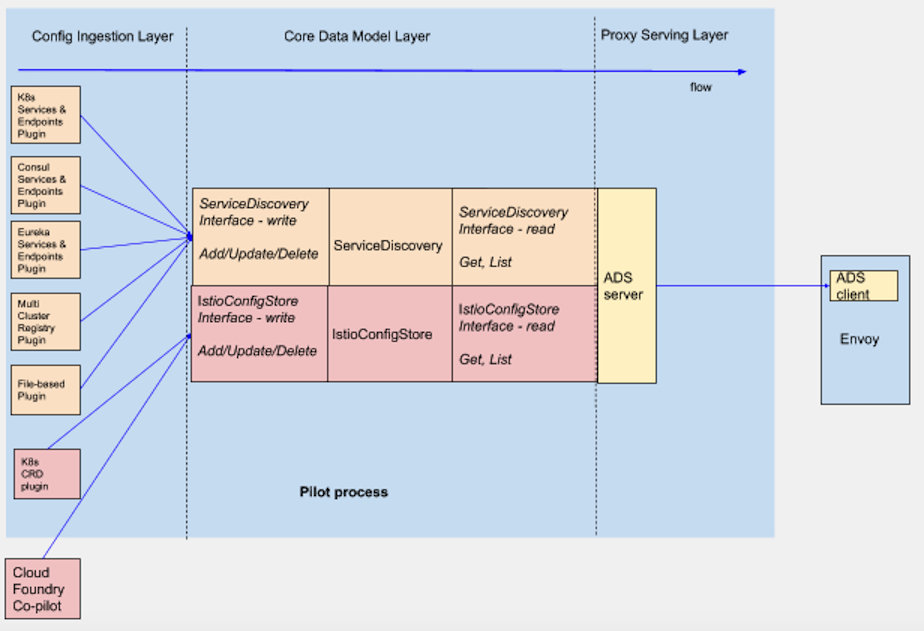
从图中可以看出 Pilot 的处理流程可以抽象为 3 层:
1.1 Config Ingestion Layer:
Pilot 关注的Config有 2 大类 (图中进行了颜色区别):
-
Istio Config: 用户侧提供的流控管理配置,特别的,在 K8s 平台中表现为 CRD, 如 VirtualService、DestinationRule 等。
-
Service Discovery Config: 服务发现配置,包括 Services、Endpoints、Nodes 等。
下文中分别以Istio Config和Service Discovery Config来表示以上 2 类数据。
Config Ingestion Layer 以插件化的方式对接各种服务发现平台,这些对接逻辑以 in-process 方式内嵌在 pilot 进程中。包括 Kubernetes, Consul, file-based config plugin, MCP 方式等。
1.2 Core Data Model Layer:
Core Data Model Layer 会缓存上一层 (Config Ingestion Layer) 获取的配置信息,根据Istio Config和Service Discovery Config数据的不同特点,该层分别使用不同的控制器对其进行处理和存储。并将来自不同平台的配置信息抽象为统一的服务发现模型,如 Service, ServiceInstance, Registry 等。
1.3 Proxy Serving Layer:
Proxy Serving Layer 负责将上层 (Core Data Model Layer) 的抽象模型,转换为具体的 xDS 协议数据,并下发到订阅这些数据的数据面。
本文将尝试对pilot-discovery discovery的处理流程进行分析,重点关注 pilot 对 k8s 平台的适配实现。后续将对 Config 转换为 Pilot Model 和 xDS 进行分析。
2. pilot 初始化流程
命令pilot-discovery discovery将创建并启动 discoveryServer:
// Create the server for the discovery service.
discoveryServer, err := bootstrap.NewServer(serverArgs)
......
// Start the server
if err := discoveryServer.Start(stop); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start discovery service: %v", err)
}
其中函数bootstrap.NewServer按照以下顺序对 discoveryServer 进行初始化,步骤清晰明了:
// 略掉错误处理代码
func NewServer(args PilotArgs) (*Server, error) {
......
//对于 k8s 平台场景,初始化 kubeClient, 后续使用
s.initKubeClient(&args);
// 网格初始化
s.initMesh(&args);
s.initMeshNetworks(&args)
// 初始化处理 Istio Config 的控制器
s.initConfigController(&args)
// 初始化处理 Service Discovery Config 的控制器
s.initServiceControllers(&args)
// 初始化 xDS 服务端
s.initDiscoveryService(&args)
s.initMonitor(&args)
s.initClusterRegistries(&args)
......
}
3. 网格配置初始化
Config 一词在源码中使用泛滥,除了上面提及的:Istio Config和Service Discovery Config外,Istio 还有 2 个全局配置集:
-
mesh:该配置集为数据面 envoy 实例提供全局的配置 (由 pilot 下发), 包括 mixer 地址,是否开启链路跟踪,以及其他重要配置开关和默认值等。
参考配置说明:https://istio.io/docs/reference/config/istio.mesh.v1alpha1/#MeshConfig
-
meshNetworks:该配置集提供了多集群 mesh 中网络配置,主要包括如何在三层网络中路由到各网络的 endpoints, 以及各网络独立的服务发现配置。
参考配置说明:https://istio.io/docs/reference/config/istio.mesh.v1alpha1/#MeshNetworks
我们称以上 2 个配置集为「网格配置」, 在源码中,网格配置初始化入口:
s.initMesh(&args);
s.initMeshNetworks(&args)
istio 控制面使用一个名为「istio」的 config map, 作为网格的全局配置:
% kubectl -n istio-system get configmap istio -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
mesh:
......
meshNetworks:
......
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: istio
namespace: istio-system
该 configmap 的 2 个 data 域「mesh」和「meshNetworks」, 分别对应上面的 2 个网格配置集:. 用户可以通过修改该 ConfigMap, 进行网格特定行为调整。
在 pilot 容器定义中,默认会将该 ConfigMap 挂载到/etc/istio/config目录,2 个配置集文件将分别位于/etc/istio/config/mesh和/etc/istio/config/meshNetworks
image: gcr.io/istio-release/pilot
......
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/istio/config
name: config-volume
......
volumes:
- configMap:
name: istio
name: config-volume
该 configMap 作为投射卷 (projected volume) , kubernetes 会自动维护 ConfigMap 到文件系统的更新,因此 pilot 只需要通过文件系统 watch 这 2 个配置文件变化,即可实现运行时配置动态修改,无需重启 pilot。
pilot 在 watch 到「网格配置」变化后,会触发 xDS 的重新计算,并将新的 xSD 下发到数据面,从而使得配置修改得以生效。
4. Config 控制器
控制器模式在 k8s 里使用非常广泛,典型的 k8s 控制器利用 informer/reflector 对资源进行List/Watch, 获得资源更新事件,事件对象入队列,缓存 object 到 indexer, 然后在控制循环中进行自定义处理。
Pilot 对Service Discovery Config和Istio Config两大类数据的处理,也是使用控制器模式,不过 Pilot 中 Config 控制器有特殊之处,因为适配多种平台,Config 有多种来源可能,除了 k8s informer, 还可能是 MCP, 文件系统,或者 consul client 等等。一个典型的 Config 控制器,可以用下图来描述:
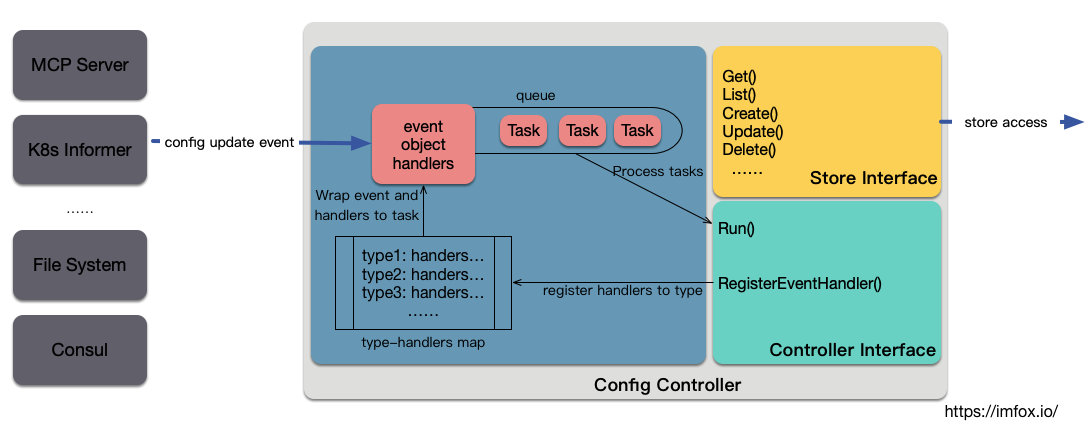
上图左边是描述 Config 来源,右边描述 Config 控制器的结构,可以划分为三个部分:
- Config 控制器要求实现「Controller interface」, 主要接口包括:为指定 config type 添加处理器,以及启动控制器消费 Task 的
Run方法。 - Config 控制器要求实现「Store Interface」, 主要包括对 config 的访问接口。write interfaces 如 Create, Update, Delete 主要是提供给 Config Ingestion Layer 使用,read interfaces 如 Get, List 主要提供给 Proxy Serving Layer 使用。
- Config 控制器还包括的其他组件:主要是 task queue 和 type-handlers 存储。
Config 控制器会按需构造特定的 config 更新事件来源,如 k8s informer、MCP 等,同时通过实现 Controller interface, 允许为不同的 config type, 添加不同的处理器链,存储到 type-handlers 中。在接收到 config 更新事件后,Pilot 会将 event、object 和该 type 对应的 handlers 包装成 Task, push 到 queue 中。最终在Run方法中启动对 queue 中 Task 的消费。
具体的,Pilot Service Discovery Config和Istio Config都按照上述控制器模式实现,下面分别介绍。
5. Istio Config 控制器
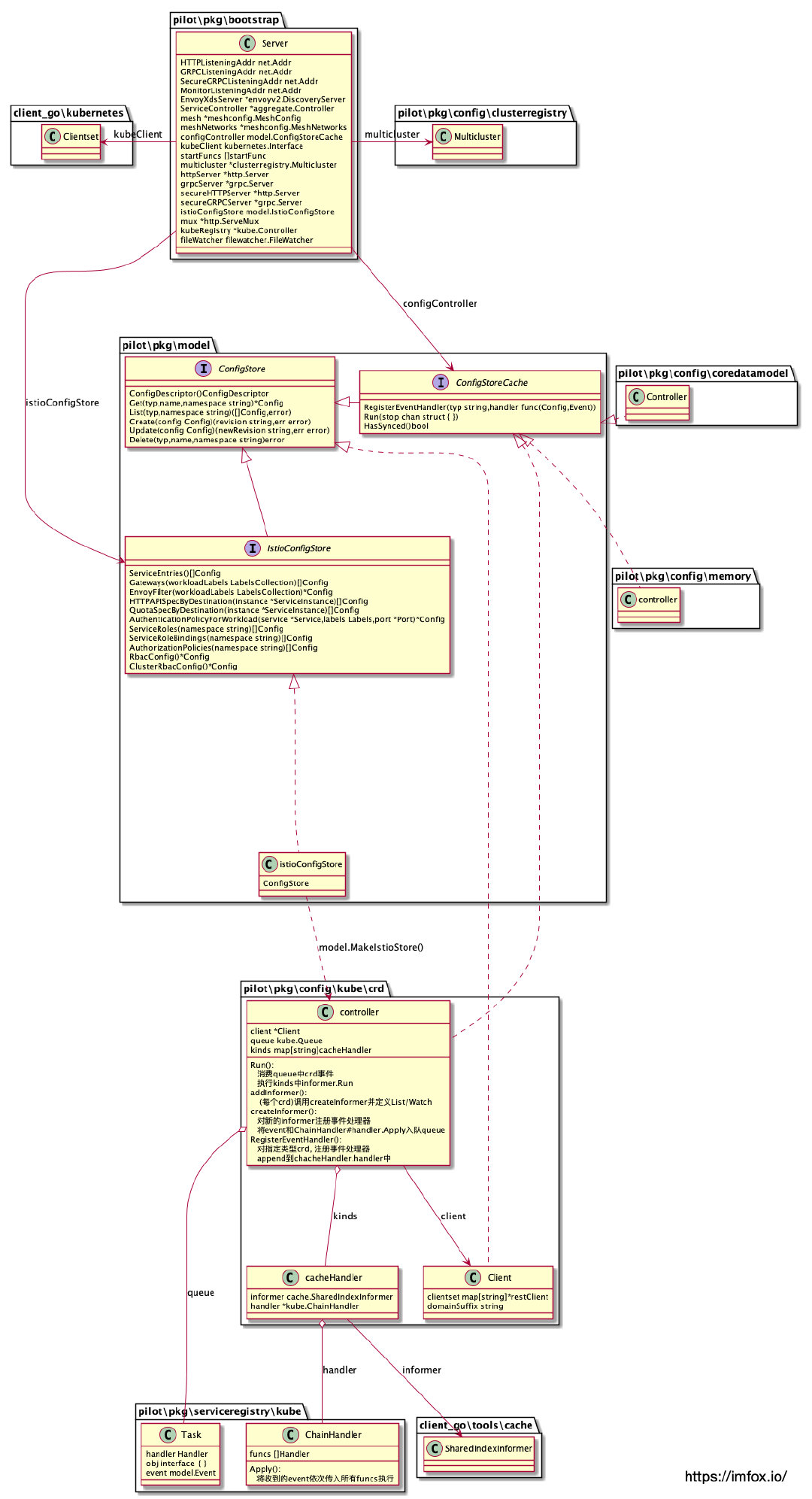
Istio Config 控制器用于处理 istio 流控 CRD, 如 VirtualService、DestinationRule 等,和 Istio Config 控制器相关的 interface 主要有:
-
pilot/pkg/model.ConfigStore
ConfigStore对象利用 client-go 库从 Kubernetes 获取 route rule、virtual service 等 CRD 形式存在控制面信息,转换为 model 包下的 Config 对象,对外提供Get、List、Create、Update、Delete等 CRUD 服务。这是一种「Store Interface」
-
pilot/pkg/model.IstioConfigStore
interface
IstioConfigStore通过 embed 方式扩展了接口ConfigStore。其主要目的是为访问 route rule、virtual service 等数据提供更加方便的接口。相对于ConfigStore提供的Get、List、Create、Update、Delete方法,IstioConfigStore 直接提供更为方便的 RouteRules、VirtualServices 等方法。这是一种「Store Interface」
-
pilot/pkg/model.ConfigStoreCache
interface
ConfigStoreCache通过 embed 方式扩展了接口ConfigStore,ConfigStoreCache的主要扩展有:注册 Config 变更事件处理函数RegisterEventHandler、开始处理流程的Run方法等。这是一种「Controller Interface」, 同时也是「Store Interface」
如上所述,inferface ConfigStoreCache包括了上一节中要求的 2 类接口,目前实现了 interface ConfigStoreCache的 Istio Config 控制器主要有以下三种:
-
以 k8s List/Watch方式获取config。
具体实现位于
pilot\pkg\config\kube\crd.controller -
以 MCP 方式从
ConfigSources获取,pilot 作为 MCP client,ConfigSources从全局配置 mesh config 中获取。具体实现位于
pilot\pkg\config\coredatamodel.Controller -
从本地文件系统中获取,主要用于测试场景。
具体实现位于
pilot\pkg\config\memory.controller
5.1 k8s List/Watch config 控制器
我们以在第一种方式 k8s List/Watch的Config 控制器为例分析:
// pilot\pkg\config\kube\crd.controller
type controller struct {
client *Client
queue kube.Queue
kinds map[string]cacheHandler
}
该 controller 同时实现了 interface IstioConfigStore和ConfigStoreCache, queue 和 kinds 属性是用于存储 Task 的队列和 type-handlers 的 map。
该 controller 对象在初始化过程中,会为指定的 istio CRD 创建一个 k8s informer, 这些 CRD 主要是:
IstioConfigTypes = ConfigDescriptor{
VirtualService,
Gateway,
ServiceEntry,
DestinationRule,
EnvoyFilter,
Sidecar,
HTTPAPISpec,
HTTPAPISpecBinding,
QuotaSpec,
QuotaSpecBinding,
AuthenticationPolicy,
AuthenticationMeshPolicy,
ServiceRole,
ServiceRoleBinding,
AuthorizationPolicy,
RbacConfig,
ClusterRbacConfig,
}
并为每个 informer 创建 EventHandler, 在 EventHandler 中会将新的 config event 包装为 Task, 并 push 到 queue 中。
Run 方法进行 queue 中 Task 消费,Task 中包括了事件类型,对象,以及处理函数链:
type Task struct {
handler Handler
obj interface{}
event model.Event
}
至此,我们看到了 event 的 生产和消费,但不涉及 event/Task 是如何消费的。
通过调用RegisterEventHandler可以添加event/Task的处理器。
但是还没有看到RegisterEventHandler的调用,也就是每种类型的 config, 有哪些处理函数,这个在下文中补充。
5.2 Istio Config UML
6. Service Discovery Config 控制器
Service Discovery Config 控制器用于处理各平台服务发现数据,如 Services、Endpoints、Nodes 等,和 Service Discovery Config 控制器相关的 interface 主要有:
-
pilot/pkg/model.ServiceDiscovery
对服务发现资源 (service/instance 等) 提供访问方法,如
Services()InstancesByPort()等。这是一种「Store Interface」
-
pilot/pkg/model.Controller
注册 Config 变更事件处理函数,包括
AppendServiceHandler()AppendInstanceHandler(), 另外还有控制器启动的Run()方法。这是一种「Controller Interface」
如上所述,只要实现了以上 2 个 interface, 就可以作为 Service Discovery Config 控制器,Pilot 中实现了以上 interface 的有:
-
对接 k8s 服务发现的控制器
具体实现位于
pilot\pkg\serviceregistry\kube.Controller -
对接 istio CRD ServiceEntry 的服务发现控制器
具体实现位于
pilot\pkg\serviceregistry\external.ServiceEntryStore -
对接 consul 服务发现的控制器
具体实现位于
pilot\pkg\serviceregistry\consul.Controller
以上控制器带上 ClusterID 后,被包装为 Registry:
// Registry specifies the collection of service registry related interfaces
type Registry struct {
// Name is the type of the registry - Kubernetes, Consul, etc.
Name serviceregistry.ServiceRegistry
// ClusterID is used when multiple registries of the same type are used,
// for example in the case of K8S multicluster.
ClusterID string
model.Controller
model.ServiceDiscovery
}
因为 Pilot 允许同时对接多个服务发现平台,因此在实际使用中会将多个 Registry 聚合在一起使用:
// pilot\pkg\serviceregistry\aggregate.Controller
type Controller struct {
registries []Registry
storeLock sync.RWMutex
}
该聚合控制器也实现了以上 2 个 interface。
6.1 k8s Service Discovery Config 控制器
下面我们重点看看 k8s Service Discovery Config 控制器的实现:
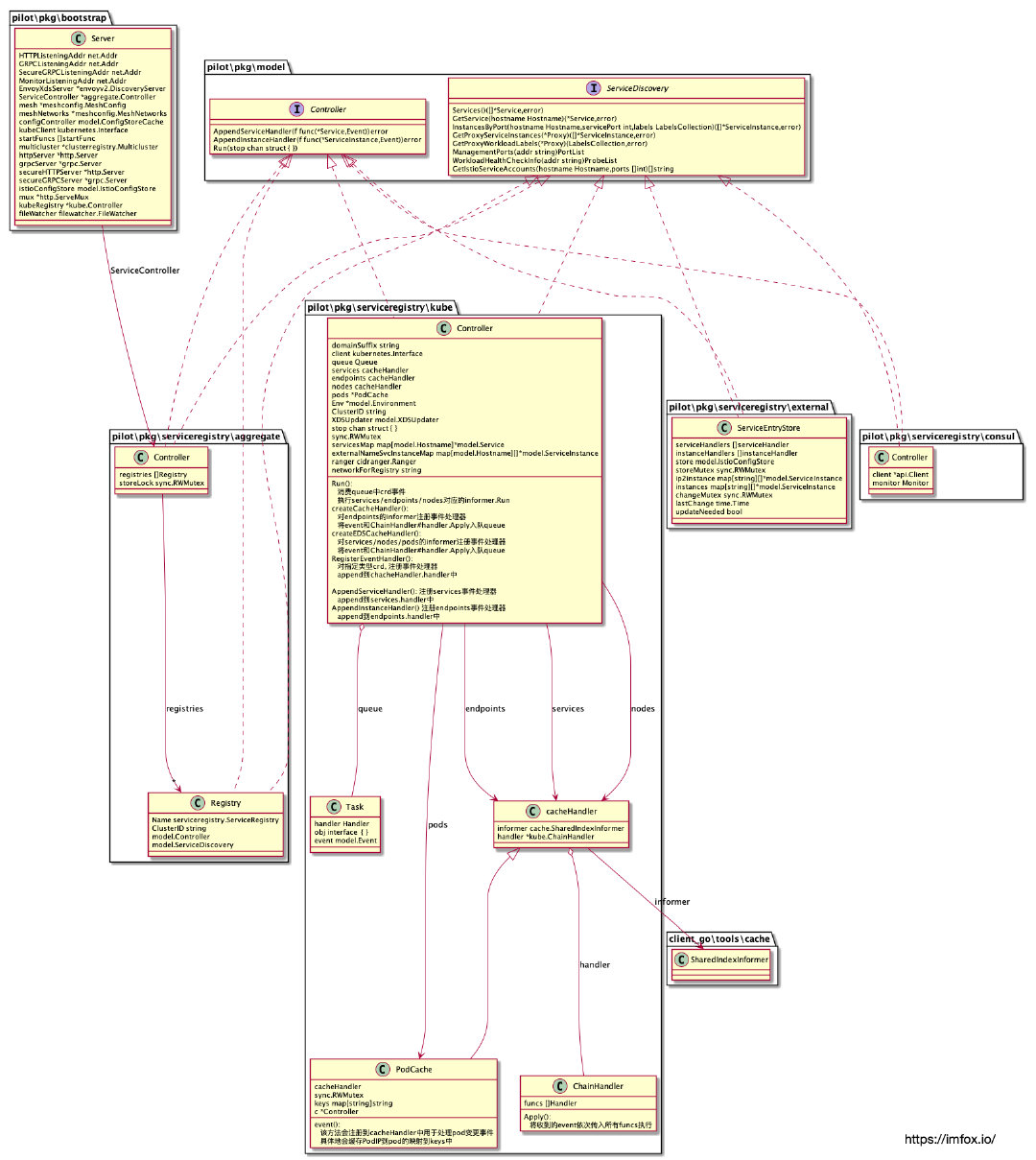
pilot\pkg\serviceregistry\kube.Controller同时实现了上述 2 个 interface, 利用 client-go 库从 Kubernetes 获取pod 、service、node、endpoint,并将这些 CRD 转换为 istio 中 Service、ServiceInstance 等统一抽象模型。
type Controller struct { // k8s service/node/ep的controller
......
queue Queue
services cacheHandler
endpoints cacheHandler
nodes cacheHandler
pods *PodCache
servicesMap map[model.Hostname]*model.Service
......
}
// NewController creates a new Kubernetes controller
// Created by bootstrap and multicluster (see secretcontroler).
func NewController(client kubernetes.Interface, options ControllerOptions) *Controller {
......
svcInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Services().Informer()
out.services = out.createCacheHandler(svcInformer, "Services")
epInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Endpoints().Informer()
out.endpoints = out.createEDSCacheHandler(epInformer, "Endpoints")
nodeInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Nodes().Informer()
out.nodes = out.createCacheHandler(nodeInformer, "Nodes")
podInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
out.pods = newPodCache(out.createCacheHandler(podInformer, "Pod"), out)
return out
}
总结主要信息:
- k8s Service Discovery Config 控制器订阅的资源变更包括:Services、Endpoints、Nodes、Pod。
- 没有统一的 type-handlers, 而是拆分到了多个属性中,如代码所示包括 Controller 的属性 services, endpoints, nodes 和 pods。
类似 Istio Config 控制器,k8s Service Discovery Config 控制器订阅的资源变更事件也会包装成 Task, push 到 queue 中等待消费,不在赘述。
6.2 Service Discovery Config UML
7. xDS 服务端
通过上述 2 类控制器,Pilot 已经可以获得Istio Config 和 Service Discovery Config的更新,接下来需要将这些不同平台的数据转换成统一的服务和路由模型,然后通过 xDS 下发给数据面代理。
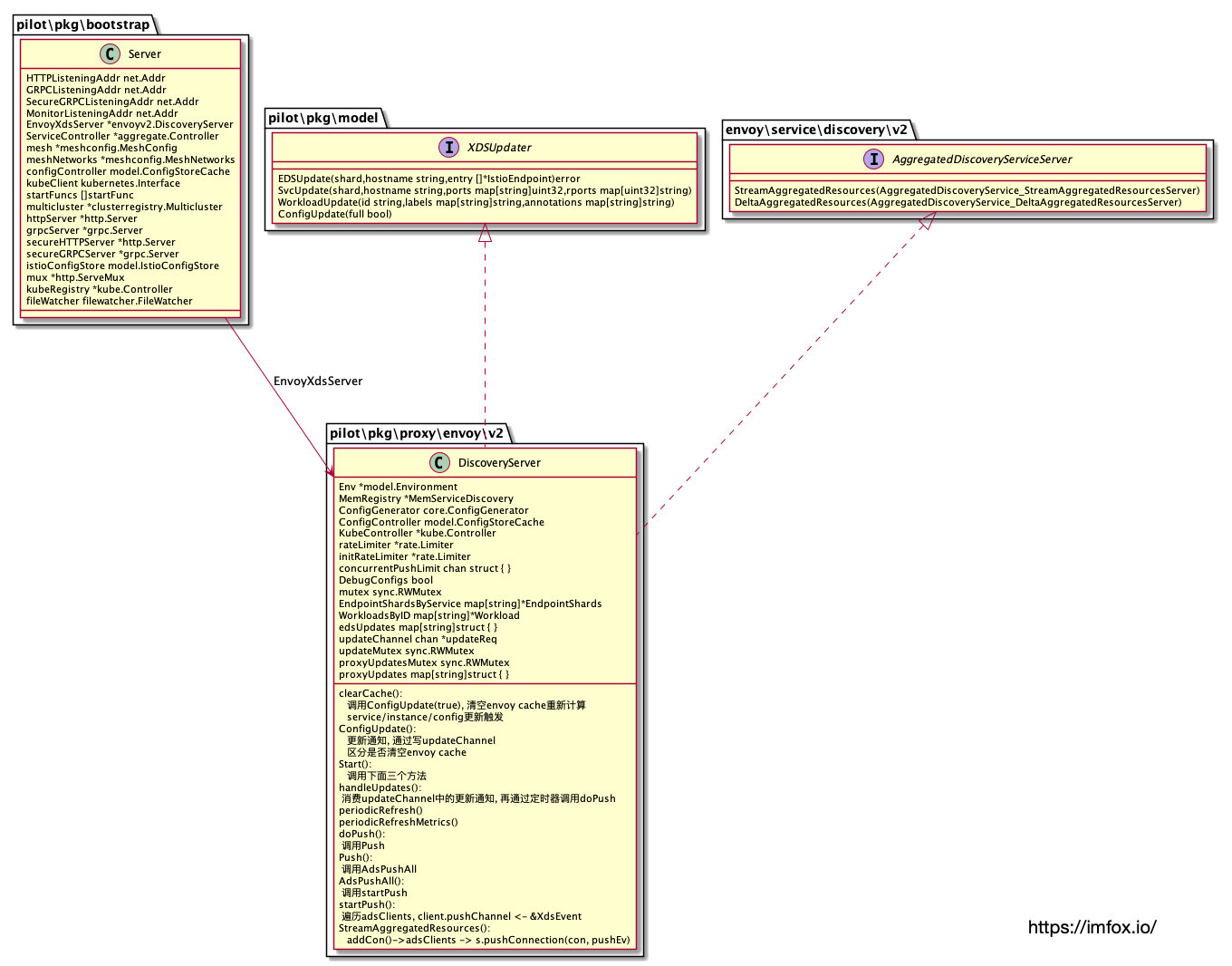
目前 pilot 默认创建一个 gRPC Server 提供 xDS 订阅服务,在 Pilot 源码里叫做 DiscoveryServer, 简单说下 DiscoveryServer 的主要逻辑:
该 gRPC Server 需要实现 2 个接口:
// AggregatedDiscoveryServiceServer is the server API for AggregatedDiscoveryService service.
type AggregatedDiscoveryServiceServer interface {
// This is a gRPC-only API.
StreamAggregatedResources(AggregatedDiscoveryService_StreamAggregatedResourcesServer) error
DeltaAggregatedResources(AggregatedDiscoveryService_DeltaAggregatedResourcesServer) error
}
接口StreamAggregatedResources主要逻辑:
-
DiscoveryServer 接受下游的订阅请求,根据请求的 xDS 类型,返回指定的资源,如 CDS/EDS/LDS/RDS。
-
DiscoveryServer 将连接对象缓存到 map 中,key 为下游 node ID 加上连接计数器。当检测到配置发生变化,将会触发这些连接上的 xDS 重新 push 到下游。这些配置变化可能是
Istio Config、Service Discovery Config或者网格全局配置集。
DeltaAggregatedResources是增量 xDS 订阅接口,目前在 istio 中还未实现。
7.1 DiscoveryServer UML
8. Pilot 演进路线
查阅社区讨论和源码分析,Pilot 目前的不足主要有这些方面:
- 多个控制面组件都依赖 istio CRD, 如 pilot, mixer 等,它们各自去订阅并处理这些 CRD, 导致各组件中代码逻辑重复,项目臃肿。
- Pilot 项目臃肿的另一个原因是,以
in-process方式对接各平台的配置获取和处理,Pilot 和这些平台之间并没有明确的接口依赖约定,istio 和其他平台出现接口和数据格式的兼容性,会是一个潜在风险。(要重视墨菲定律)。 - Pilot 性能问题:Pilot 在关注的配置发生变化后,会重新计算 xDS 数据,并触发持有连接的 xDS 全量下发,DiscoveryServer 也没有对配置变化的内容进行分析,因而存在重复和无用的 xDS push. 截止版本 1.1, 增量 xDS 订阅接口在 Pilot 中还未实现。
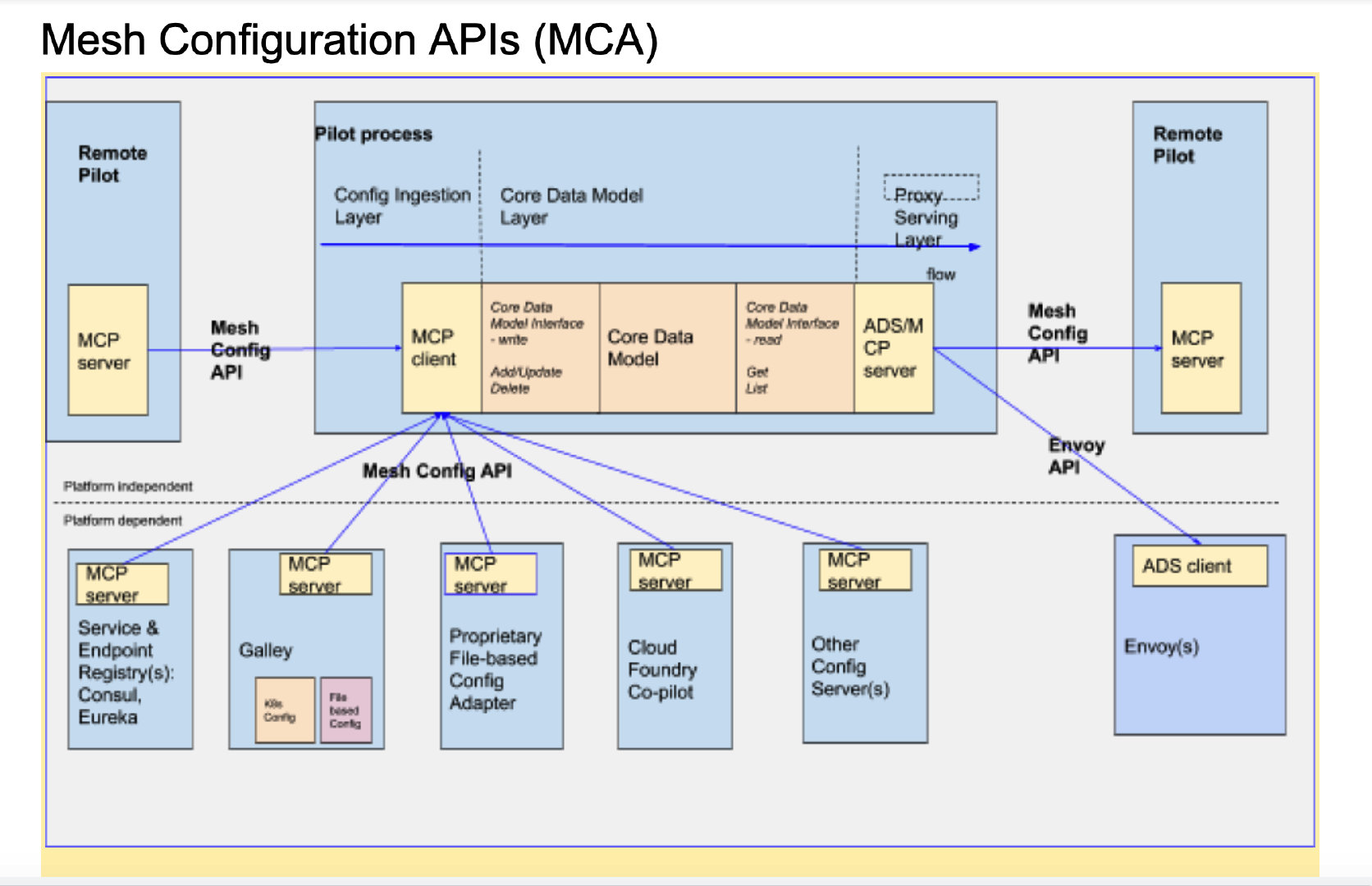
下图是社区对 Pilot 解耦的方案提议:
简要说明:
- 使用统一配置管理器 (
Galley) 来处理 istio CRD 的处理,通过 MCP 进行下发,Galley 作为 MCP 服务端,Pilot/Mixer 等作为 MCP 客户端。在 istio 1.1 中,Galley 的以上功能已经发布,并作为默认的配置处理方式,只是 1.1 中还保留了旧的实现代码,Pilot/Mixer 可以选择独立List/Watch Istio CRD, 未来随着 Galley 功能的增强和稳定,旧的实现应该会被移除。 - 提议设计新的 gRPC 双向流协议:Mesh Configuration Protocol (MCP), 对配置进行抽象,聚合和传输。(类似 xDS gRPC), 以此将 Pilot 中配置对接逻辑从 in-process 逐步改造为 out-of-process 方式。
以上对 Pilot 的能力和结构进行了分析,下一篇文章将分析 Pilot 是如何将 Config 转为为 xDS。
